Submit feedback
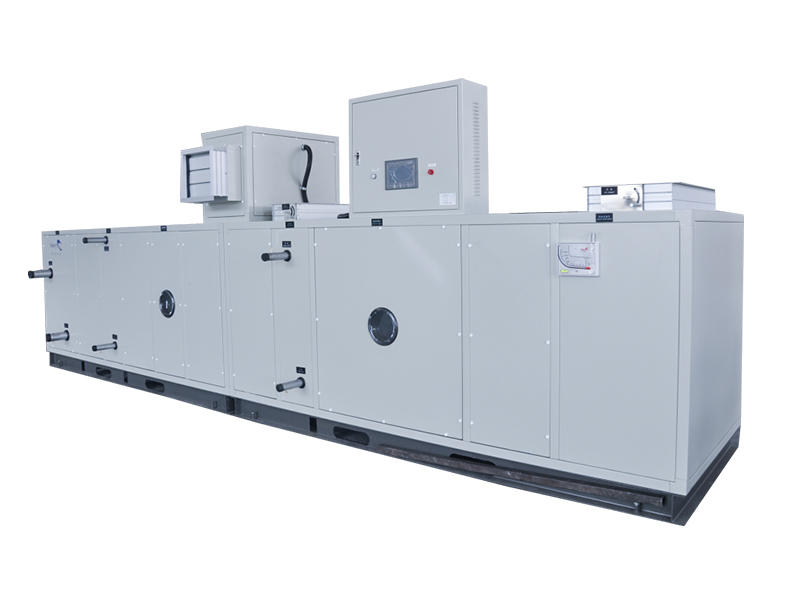
Nuclear Power Plants Rotary Dehumidification Unit Suppliers
Company Honors

Zhejiang manufacturing certificate

Certificate of Integration of Informatization and Industrialization

CE Certificate

Innovation Fund

Refrigeration and air conditioning industry governing unit

Specialized and Specialized

Excellent Science and Technology Enterprise of Zhejiang Province

Member of Hangzhou Environmental Protection Industry Association

Excellent cooperation unit

ZJU Cooperation

Outstanding Innovation Unit

Key Incubatees

-
What effect does thermal conductivity have on lithium battery dry chamber efficiency?
Thermal conductivity significantly affects the efficiency of lithium battery dry rooms. Thermal conductivity refers to the ability of a substance to transfer heat, determining the ...
2024-03-19 -
What does the dry efficiency of lithium battery drying room mainly depend on?
The drying efficiency of lithium battery dry rooms mainly depends on several aspects, which collectively determine the speed, effectiveness, and energy utilization efficiency of th...
2024-03-12 -
How does the lithium battery dry room help the development of the new energy automobile industry?
Lithium battery dry rooms play a crucial role in the development of the new energy vehicle industry. Here are several key aspects in which lithium battery dry rooms contribute to t...
2024-03-05 -
How can the design of the NMP Solvent Recovery System be customized to accommodate changes in process requirements in different industries?
The design of an NMP solvent recovery system can be customized to accommodate changes in process requirements across different industries by considering various factors related to ...
2024-02-26 -
What are the components of the NMP Solvent Recovery System and what roles do they play?
The NMP solvent recovery system comprises several key components, each serving a specific role in the recovery process. These components work together to efficiently remove NMP sol...
2024-02-23
How to Install Nuclear power plants Rotary Dehumidification Unit?
The installation process of a rotary dehumidification unit for a nuclear power plant requires specialized knowledge and skills due to the critical nature of the facility. It is important to follow proper procedures and guidelines to ensure safe and efficient installation. Here are some general steps that are typically involved in the installation of a rotary dehumidification unit for a nuclear power plant:
Site preparation: Before the installation process can begin, the site must be prepared for the equipment. This involves ensuring that the installation area is clean, dry, and free of any debris or obstructions that may impede the installation process.
Equipment delivery: Once the site is ready, the equipment is delivered to the site. The dehumidification unit is typically delivered in pre-fabricated sections and assembled on-site.
Positioning of the unit: The unit is then positioned in the designated area, and the supporting structure is erected to hold the unit in place. The unit is typically anchored to the foundation to prevent any movement during operation.
Installation of the electrical and mechanical components: Once the unit is in place, the electrical and mechanical components are installed. This includes wiring and connecting the control systems, fans, filters, and other necessary components.
Testing and commissioning: After the installation is complete, the unit is tested to ensure it is functioning correctly. This includes testing the electrical and mechanical systems, adjusting the controls, and verifying the performance of the dehumidification unit. Once the unit passes all tests, it is commissioned for use.
Maintenance and ongoing support: Once the dehumidification unit is operational, it is important to establish a maintenance and support plan. This includes regular inspections, cleaning, and replacement of components to ensure the unit continues to function correctly.
It is important to note that the installation of a rotary dehumidification unit for a nuclear power plant should only be carried out by trained and experienced professionals who have a thorough understanding of the equipment and the facility's unique requirements. Proper installation is essential to ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of the power plant's operations.
The Structure of Nuclear power plants Rotary Dehumidification Unit
The rotary dehumidification unit in a nuclear power plant is a critical component of the plant's cooling system. Its primary purpose is to remove moisture from the air circulating through the plant, which helps to prevent corrosion and other damage to the plant's equipment.
The rotary dehumidification unit consists of several key components, including:
Desiccant wheel: This is a rotating wheel made of a material that can absorb moisture, such as silica gel or molecular sieves. The desiccant wheel is typically divided into two sections, with one section absorbing moisture from the incoming air and the other section regenerating by heating to release the moisture.
Air handling unit: This unit is responsible for circulating the air through the plant and directing it to the desiccant wheel. It typically consists of fans, ductwork, filters, and dampers to control the airflow.
Heating and cooling coils: These coils are used to control the temperature of the air circulating through the plant. They are typically located upstream of the desiccant wheel to prevent moisture from condensing on them.
Controls and sensors: These components monitor and control the operation of the dehumidification unit, including the temperature and humidity levels in the plant.
Overall, the rotary dehumidification unit is a critical component of the nuclear power plant's cooling system, as it helps to maintain a dry environment that is essential for preventing corrosion and other damage to the plant's equipment.



 English
English 简体中文
简体中文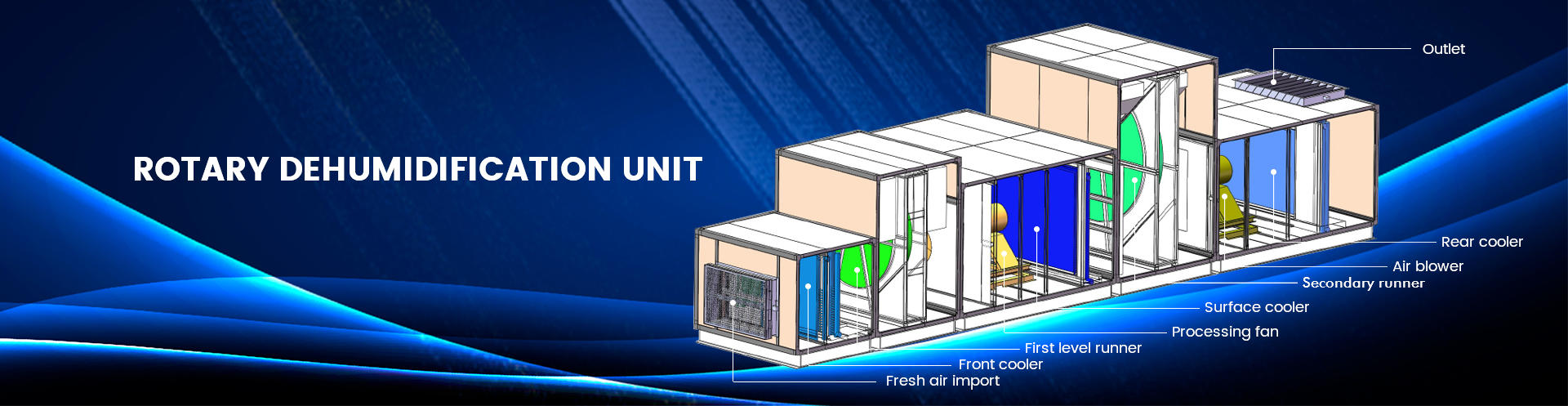





 View All
View All
